Butyric acid or butanoic acid is a fatty acid, therefore a carboxylic acid, with a straight carbon-chain of four carbon atoms.
Its name derives from the Greek word βούτυρος, meaning butter, from which it was first isolated.
It is present in plant and animal tissues in small amounts, mostly as a component of triglycerides.
In mammals, it is mainly produced by the anaerobic fermentation of fibers and resistant starch by bacteria of the gut microbiota, although small mounts may be produced from amino acids and endogenous synthesis.[5][13]
It is absorbed almost entirely by colonocytes, for which it is a major source of energy[12].
Butyric acid also have regulatory roles, both at the gastrointestinal and systemic levels, resulting from the binding to specific receptors or from its use as an acyl group donor in histone acylations.[3][14]
Contents
Chemical properties
Butyric acid has a molecular weight of 88.11 g/mol, molecular formula C4H8O2, condensed formula CH3CH2CH2COOH, and shorthand notation 4:0.[9]
Its conjugate base, known as butyrate or butanoate ion, has condensed formula CH3CH2CH2COO– and represents the form in which the free fatty acid, with a pKa of 4.8, exists in biological systems at physiological pH.
As its carbon-chain has no double bonds, butyric acid belongs to the group of saturated fatty acids. Furthermore, as the number of carbon atoms in the carbon-chain is less than 6, it is a short-chain fatty acid (SCFA), like acetic acid, propionic acid, and valeric acid, which are straight-chain fatty acids, and isobutyric acid, isovaleric acid and 2-methylbutyric acid, which instead are branched-chain fatty acids. Note that butyric acid and isobutyric acid, which have the molecular formula C4H8O2, are an example of structural isomerism.
The short carbon chain of butyrate influences its physical properties. In fact, its small size means that the polarity of the carboxyl group wins, which makes the fatty acid soluble in polar solvents such as water and ethanol.[12]
At room temperature, it appears as a colorless oily liquid, with an unpleasant and penetrating odor.[9] Conversely, its low molecular weight esters, such as methyl butyrate, often have pleasant tastes or aromas, and are used as additives in the food and perfume industries[6].
Its melting point is -7.9 °C (17.78 °F; 265.25 K), while its boiling point is 163.5 °C (326.3 °F; 436.65 K).[9]
Dietary sources
Butyric acid, like other fatty acids, is present in plant and animal tissues mostly as a component of triglycerides, although in much lower amounts than long-chain fatty acids. Like other SCFAs, butyrate is mainly esterified in sn-3 position of the triglycerides.
In adults, the main food source is milk and dairy products, in which it is the most abundant short-chain fatty acid.[1] The unpleasant smell of rancid butter is due to its release, through hydrolysis, from triglycerides.
Breast milk is the main source for breastfed infants.[1][12]
During lipid digestion, butyrate is released from triglycerides mainly through the action of lingual lipase. The enzyme, produced and secreted by serous lingual glands, leads to the release of a single fatty acid, preferably belonging to the group of short-chain fatty acids or medium-chain fatty acids.
However, in most mammals, including humans, the quantitatively most important source is the anaerobic fermentation of fibers and resistant starch which occurs in the cecum and colon by bacterial species of the phylum Firmicutes.[13] Approximately 300-360 mM of butyrate are produced per day, out of a total of 500-600 mM of short-chain fatty acids produced, with the remaining amounts divided between acetic acid and propionic acid, therefore approximately 100-120 mM each,[11][13] corresponding to a molar ratio of about 60:20:20, respectively.
Like other short-chain fatty acids, butyrate concentration is higher in the cecum and proximal colon than in the distal parts of the intestine, as the substrates for its synthesis are depleted.[7]
Biosynthesis
Butyric acid can be synthesized by bacteria in the cecum and colon, or originate from endogenous synthesis, mainly in the liver.
During carbohydrate digestion, fiber and resistant starch are undigested as humans lack the enzymes needed for their catabolism. In the large intestine, fiber and resistant starch are catabolized by bacteria of the gut microbiota which, as a whole, code for more than 260 different glycoside hydrolases which are able to hydrolyze the indigestible carbohydrates into their constituent monosaccharides, namely, pentoses, hexoses and deoxyhexoses. Then, pentoses enter the pentose phosphate pathway, hexoses and deoxyhexoses enter glycolysis, to lead to pyruvate generation. Pyruvate, the conjugate base of pyruvic acid, is the main precursor of butyric acid, as well as of other SCFAs produced by intestinal bacteria.[8][10]
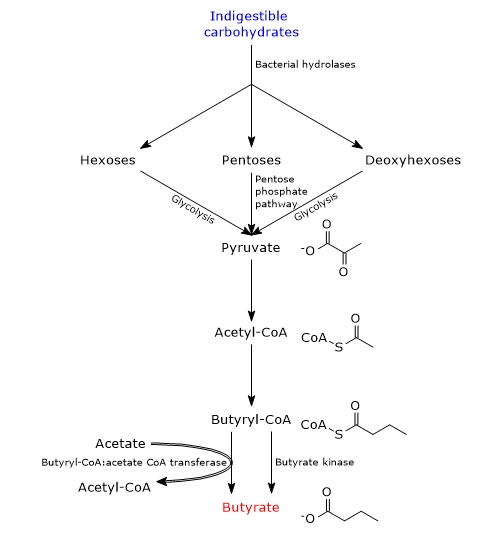 To a small extent, butyrate can also be synthesized from amino acids.
To a small extent, butyrate can also be synthesized from amino acids.
The synthesis of butyric acid by intestinal bacteria is influenced, like that of other SCFAs produced by several factors. Resulting from the anaerobic fermentation of indigestible polysaccharides, the amounts of fiber in the intestinal lumen, in particular resistant starch, positively affects its synthesis. Therefore, a high fiber diet, such as the Mediterranean diet, may be a predisposing factor. Intestinal transit time is also important.
As butyric acid is mainly produced by bacteria of the phylum Firmicutes, hence, the composition of the gut microbiota is able to influence its synthesis.[2]
The pH of the intestinal lumen is also important; in fact, butyrate-producing bacteria dominate at a pH value around 5.5, whereas acetate and propionate-producing bacteria, which mainly belong to the phylum Bacteroides, dominate at pH value around 6.5.[7]
Synthesis from fibers and resistant starch
In bacteria, there are two pathways for butyrate synthesis from indigestible carbohydrates.[11][12]
In most butyrate-producing bacteria, the fatty acid is produced through a metabolic pathway that begins with the condensation of two acetyl-CoA molecules to acetoacetyl-CoA, in the reaction catalyzed by acetyl-CoA acetyltransferase (EC 2.3.1.9). Subsequently:
- acetoacetyl-CoA is converted into beta-hydroxybutyryl-CoA, in the reaction catalyzed by beta-hydroxybutyryl-CoA dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.157);
- beta-hydroxybutyryl-CoA is converted into crotonyl-CoA, in the reaction catalyzed by crotonase (EC 4.2.1.17);
- crotonyl-CoA is converted into butyryl-CoA, in the reaction catalyzed by butyryl-CoA dehydrogenase (EC 1.3.1.86);
- in the last step, butyryl-CoA is converted into butyrate in the reaction catalyzed by butyryl-CoA:acetate CoA transferase (EC 2.8.3.8). In this reaction, an exogenous acetate acts as coenzyme A acceptor.[4]
In a small number of butyric acid-producing bacteria, butyryl-CoA is converted to butyryl phosphate in the reaction catalyzed by phosphate butyryltransferase (EC 2.3.1.19). In the last step, catalyzed by butyrate kinase (EC 2.7.2.7), butyrate is released and an ATP molecule is made.[2]
Synthesis from amino acids
Like other short-chain fatty acids, butyric acid can be produced, in small amounts, from amino acids resulting from protein degradation. This synthesis occurs in the distal part of the colon, often by non-commensal bacteria.[5]
Amino acids that can act as butyrate precursor are:
- glutamic acid, an acidic amino acid, and the basic amino acids lysine, arginine and histidine, all precursors of acetic acid as well;
- the sulphur-containing amino acids cysteine and methionine, from which, acetic acid and propionic acid, and propionic acid, respectively, can also be produced.[7]
Protein metabolism by gut bacteria, from the degradation of proteins into the constituent amino acids onward, is influenced by the pH of the intestinal lumen, and is more likely at neutral or weakly alkaline pH, unlike what happens with butyrate synthesis from fibers and resistant starch.[7]
Endogenous synthesis
Butyric acid can also derive from endogenous synthesis, mainly in the liver, via two pathways. It can be produced through cycles of beta-oxidation of fatty acids with longer carbon chains,[10] or it can derive from de novo synthesis.[14]
Intestinal absorption
About 90-95 percent of the butyric acid produced by gut bacteria is absorbed in the cecum and colon, while the remaining small percentage is lost in the feces, like other short-chain fatty acids[16].
Butyrate entry into colonocytes can occur by passive diffusion, or can be mediated by MCT1, MCT4, SMCT1 and BCRP transporters.[11][14] The transporters are located on the apical surface of the cell, and their synthesis can be regulated by butyrate-sensitive receptors present on the cell surface. They are able to strongly increase the entry of the fatty acid into the cell.
Transport
The small amount of butyric acid not used by colonocytes leaves the cell at the basolateral membrane, by active transport and passive diffusion, to enter the portal circulation, like the other two main short-chain fatty acids. In the portal circulation, butyrate reaches a concentration of around 30 mM/L, similar to that reached by propionate, but much lower than that of acetate, which is around 260 mlM/L.[7]
A small amounts of these lipids also reaches the rectum, where, they are absorbed and used by colonocytes, while the unused ones pass into the systemic circulation via the internal iliac vein, thus bypassing the portal system and therefore the liver.[15]
Butyrate, like other SCFAs, is present in the circulation in free form, namely, as a non-esterified fatty acid, and, bound to the plasma protein albumin, reaches the liver and other organs. Cell uptake, as well as intracellular transport, does not require specific transport proteins.[12]
Role
In colonocytes, butyrate is used for energy and performs also regulatory functions, which result from the binding to protein receptors or from its use in histone acylation reactions.[11][14][15]
The fatty acid not that reaches the liver and, in a small amount, equal to about 2 percent of absorbed fatty acid, the peripheral tissues, performs regulatory functions.
Energy role
Butyric acid is the preferred energy source of colonocytes, which actively metabolized it through beta-oxidation, the citric acid cycle and oxidative phosphorylation. In this way, the fatty acid contributes, for example, to the maintenance of cellular homeostasis and the integrity of the tight junctions, and therefore to the integrity of the intestinal barrier.[5]
Once inside the mitochondrion, it is converted to butyryl-CoA in the reaction catalyzed by two members of the Acyl-CoA synthetase short-chain family (EC 6.2.1.1), referred to as ACSS1 and ACSS3.[14]
Butyryl-CoA enters beta-oxidation, the first step of which can be catalyzed by a short-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase (EC 1.3.8.1), but also by a medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase (EC 1.3.8.7), which can act on fatty acids of 4 to 14 carbons.[14] These dehydrogenases require FAD as coenzyme, whereas the other dehydrogenase involved in the beta-oxidation, beta-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.35), requires NAD as a coenzyme.
Acetyl-CoA enters the citric acid cycle at the level of citrate synthase (EC 2.3.3.1), enzyme that catalyzes the condensation between oxaloacetate and acetyl-CoA to form citrate. The carbon chain of acetyl-CoA is then oxidized to two carbon dioxide molecules, with production of one GTP, three NADH and one FADH2.
In the next step the electron transfer from NADH and FADH2 to the molecular oxygen by the mitochondrial respiratory chain occurs, electron transport which is coupled to the creation of a transmembrane proton gradient.
Finally, ATP synthase uses the energy stored in the proton gradient to synthesize ATP from ADP.
Histone acylation
Histone acylations and deacylations are reactions that involve the ε-position of the lysine side chains present in the N-terminal tail, and play a major role in the regulation of gene expression in eukaryotic cells.
In general, acylations are catalyzed by acyltransferases (EC 2.3-); in particular acetylations are catalyzed by histone acetyltransferases (EC 2.3.1.48), while deacylations by hydrolases, such as histone deacetylases (EC 3.5.1.98).
The acylation of the lysine side chain neutralize some of the positive charges of the histones, making the nucleosome less compact, thus elevating DNA accessibility and therefore facilitating gene expression.
Butyric acid contributes to histone acylations in at least three ways.[14]
- The presence in the cytosol of a short-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase, ACSS2, allows the synthesis of butyryl-CoA which, once in the nucleus, can be used as an acyl group donor. Note that butyryl-CoA of cytosolic origin can also enter the mitochondrion, and that of mitochondrial origin pass into the cytosol, by carnitine/acyl-carnitine translocase.
- Butyryl-CoA can be oxidized to acetyl-CoA, thus contributing to acetylations.
- Finally, butyrate can inhibit the activity of histone deacetylases,[7] an ability shared with other short-chain fatty acids, although the efficiencies are different:
up to 80% for butyric acid;
up to 60% for propionic acid;
acetic acid has the least inhibitory effect.
This mode of action on histone deacetylases has been observed not only in the intestine and associated immune tissue but also, for example, at the liver level, where butyrate, by inhibiting histone deacetylase 2, increases the expression of the GPL-1 receptor, which potentiates the effects of GPL-1 on the inhibition of lipid synthesis and increasing of fatty acid oxidation.[14][17]
Membrane receptors
The regulatory functions of butyric acid, like for other short-chain fatty acids, also result from the binding to specific protein receptors, namely, the G protein-coupled receptors, such as GPR109A, GPR41, GPR43.[3] The different SCFAs have different abilities to activate the receptors: GPR109A is more likely to be activated by butyrate, GPR41 by butyrate and propionate, while GPR43 by acetate and propionate.
The binding to the receptor causes different effects depending on the cell type. At the gastrointestinal level, butyrate binds to receptors present on the apical surface of L cells, stimulating the production of hormones such as peptide YY and GLP-1, which are involved in the regulation of satiety and food intake [13]. Butyrate also binds to receptors on enterochromaffin cells, stimulating the release of serotonin, a hormone that may influence intestinal motility. In the pancreas, it increases insulin release by binding to receptors on beta cells.[13]
At systemic levels, it may influence the development, differentiation and activation of immune system cells.
References
- ^ a b Chow Ching K. Fatty acids in foods and their health implication. 3th Edition. CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group, 2008
- ^ a b Deleu S., Machiels K., Raes J., Verbeke K., Vermeire S. Short chain fatty acids and its producing organisms: an overlooked therapy for IBD? EBioMedicine 2021;66:103293. doi:10.1016/j.ebiom.2021.103293
- ^ a b Fagundes R.R., Belt S.C., Bakker B.M., Dijkstra G., Harmsen H.J.M., Faber K.N. Beyond butyrate: microbial fiber metabolism supporting colonic epithelial homeostasis. Trends Microbiol 2023:S0966-842X(23)00226-3. doi:10.1016/j.tim.2023.07.014
- ^ KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes. Butanoate metabolism. https://www.genome.jp/pathway/map00650+C00136
- ^ a b c Koh A., De Vadder F., Kovatcheva-Datchary P., Bäckhed F. From dietary fiber to host physiology: short-chain fatty acids as key bacterial metabolites. Cell 2016;165(6):1332-1345. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2016.05.041
- ^ Kubitschke J., Lange H., Strutz H. Carboxylic acids, aliphatic. Ullmann’s encyclopedia of industrial chemistry. Wiley-VCH. 2014 doi:10.1002/14356007.a05_235.pub2
- ^ a b c d e f Liu X.F., Shao J.H., Liao Y.T., Wang L.N., Jia Y., Dong P.J., Liu Z.Z., He D.D., Li C., Zhang X. Regulation of short-chain fatty acids in the immune system. Front Immunol 2023;14:1186892. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2023.1186892
- ^ Macfarlane S., Macfarlane G.T. Regulation of short-chain fatty acid production. Proc Nutr Soc 2003;62(1):67-72. doi:10.1079/PNS2002207
- ^ a b c National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Compound Summary for CID 264, Butyric Acid. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Butyric-Acid. Accessed Sept. 24, 2023
- ^ a b Nelson D.L., Cox M.M. Lehninger. Principles of biochemistry. 6th Edition. W.H. Freeman and Company, 2012.
- ^ a b c d Portincasa P., Bonfrate L., Vacca M., De Angelis M., Farella I., Lanza E., Khalil M.,Wang D.Q.-H., Sperandio M., Di Ciaula A. Gut microbiota and short chain fatty acids: implications in glucose homeostasis. Int J Mol Sci 2022;23:1105. doi:10.3390/ijms23031105
- ^ a b c d e Schönfeld P., Wojtczak L. Short- and medium-chain fatty acids in energy metabolism: the cellular perspective. J Lipid Res 2016;57(6):943-54. doi:10.1194/jlr.R067629
- ^ a b c d e Silva Y.P., Bernardi A., Frozza R.L. The role of short-chain fatty acids from gut microbiota in gut-brain communication. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2020;11:25. doi:10.3389/fendo.2020.00025
- ^ a b c d e f g h Trefely S., Lovell C.D., Snyder N.W., Wellen K.E. Compartmentalised acyl-CoA metabolism and roles in chromatin regulation. Mol Metab 2020;38:100941. doi:10.1016/j.molmet.2020.01.005
- ^ a b van der Beek C.M., Dejong C.H.C., Troost F.J., Masclee A.A.M., Lenaerts K. Role of short-chain fatty acids in colonic inflammation, carcinogenesis, and mucosal protection and healing. Nutr Rev 2017;75(4):286-305. doi:10.1093/nutrit/nuw067
- ^ Xiong R.G., Zhou D.D., Wu S.X., Huang S.Y., Saimaiti A., Yang Z.J., Shang A., Zhao C.N., Gan R.Y., Li H.B. Health benefits and side effects of short-chain fatty acids. Foods 2022;11(18):2863. doi: 10.3390/foods11182863
- ^ Zhao Z.H., Wang Z.X., Zhou D., Han Y., Ma F., Hu Z., Xin F.Z., Liu X.L., Ren T.Y., Zhang F., Xue Y., Cui A., Liu Z., Bai J., Liu Y., Cai G., Su W., Dai X., Shen F., Pan Q., Li Y., Fan J.G. Sodium butyrate supplementation inhibits hepatic steatosis by stimulating liver kinase B1 and insulin-induced gene. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol 2021;12(3):857-871. doi:10.1016/j.jcmgh.2021.05.006